Introduction
Fraud is a significant risk for businesses, leading to financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. Organizations must develop proactive fraud detection strategies to safeguard their assets. A combination of risk assessments, monitoring programs, and employee engagement can significantly reduce fraud risks.
This article explores top strategies that businesses can implement to detect and prevent fraud effectively.
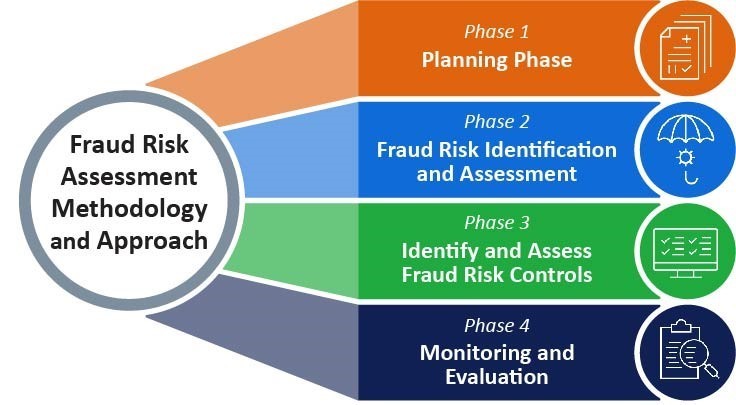
Conducting a Fraud Risk Assessment (FRA)
A Fraud Risk Assessment (FRA) is the first line of defense in identifying and mitigating fraud risks. It helps businesses pinpoint vulnerabilities and develop appropriate safeguards.
Steps to Conduct an Effective FRA:
Below is the list of steps one can follow to conduct risk assessment from fraud perspective.
- Identify Key Fraud Risks:
- Assess areas like payroll, procurement, financial reporting, and vendor management.
- Example: A company discovers that vendor invoices are frequently altered, leading to duplicate payments.
- Prioritize Risks Based on Likelihood and Impact:
- Use a risk matrix to categorize risks as low, medium, or high.
- Example: Cyber fraud may have a lower likelihood but a catastrophic financial impact.
- Develop Controls to Mitigate Risks:
- Implement segregation of duties, approval workflows, and transaction limits.
- Example: A manufacturing firm reduces fraud by requiring dual approvals for high-value purchases.
Leveraging Continuous Monitoring Programs
Continuous monitoring ensures that fraud indicators are identified in real-time, allowing organizations to respond swiftly.
Techniques for Continuous Monitoring:
- Data Analytics for Pattern Recognition:
- Analyze transactions for anomalies, such as duplicate payments or unusual spending patterns.
- Example: A bank detects repeated small withdrawals from multiple accounts, signaling potential money laundering.
- Automated Alerts and Dashboards:
- Set up real-time fraud alerts for high-risk transactions.
- Example: An AI-driven system alerts the compliance team when an employee expense exceeds policy limits.
- Audit Trail Analysis:
- Track system logins, approvals, and modifications to detect unauthorized access.
- Example: An IT security team identifies an employee attempting to override financial controls.
Strengthening Internal Controls
Robust internal controls prevent fraudulent activities by reducing the opportunity for misconduct.
Essential Internal Controls:
- Segregation of Duties:
- Ensure that critical financial functions are not handled by a single individual.
- Example: A finance team requires different employees to authorize and process payments.
- Whistleblower Programs:
- Encourage employees to report suspicious activities anonymously.
- Example: A supplier fraud case is uncovered through an anonymous tip-off from an internal employee.
- Regular Audits and Spot Checks:
- Conduct unannounced audits to detect fraudulent transactions.
- Example: A retail chain discovers cash discrepancies through a surprise audit.
Employee Training and Fraud Awareness Programs
Employees play a critical role in fraud detection and prevention. Companies should invest in fraud awareness training to empower staff with knowledge on identifying fraudulent activities.
Key Aspects of Fraud Awareness Training:
- Recognizing Red Flags:
- Educate employees on common fraud schemes such as payroll fraud, expense fraud, and vendor kickbacks.
- Example: A procurement officer identifies inflated invoices after fraud training.
- Encouraging Ethical Behavior:
- Promote a culture of integrity and accountability.
- Example: A company introduces an ethics hotline to report fraudulent behavior anonymously.
- Simulated Fraud Scenarios:
- Conduct practical exercises and case studies to test employees’ fraud detection skills.
- Example: A finance team participates in a mock fraud investigation to improve fraud detection abilities.
Utilizing Advanced Technology for Fraud Detection
Technology-driven solutions can enhance an organization’s fraud detection capabilities by leveraging AI, machine learning, and blockchain.
Key Fraud Detection Technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
- Identify fraudulent patterns and anomalies in financial transactions.
- Example: An AI system detects fraudulent insurance claims by analyzing past claim patterns.
- Blockchain for Secure Transactions:
- Use blockchain to create tamper-proof transaction records.
- Example: A logistics company prevents supply chain fraud by using blockchain to track shipments.
- Behavioral Analytics:
- Monitor employee behavior for suspicious activities, such as sudden changes in financial activities.
- Example: An HR system flags an employee attempting to access payroll records outside business hours.
Establishing Fraud Response Protocols
Even with preventive measures, organizations must be prepared to respond to fraud incidents effectively.
Steps to a Strong Fraud Response Plan:
- Incident Investigation:
- Conduct a thorough investigation to determine the extent of fraud.
- Example: A forensic audit team traces financial discrepancies to an unauthorized wire transfer.
- Corrective Action and Recovery:
- Take disciplinary action and strengthen controls to prevent recurrence.
- Example: A firm implements tighter financial controls after uncovering an employee theft case.
- Regulatory Compliance Reporting:
- Ensure compliance with legal and regulatory frameworks.
- Example: A financial institution reports fraud cases to regulators to maintain compliance.
Conclusion: A Proactive Approach to Fraud Prevention
Organizations must take a proactive approach to fraud detection by implementing risk assessments, continuous monitoring, strong internal controls, and advanced technology.
By integrating these strategies, businesses can safeguard assets, maintain compliance, and enhance operational integrity.
Key Takeaways:
✔ Conduct regular Fraud Risk Assessments to identify vulnerabilities.
✔ Implement real-time Continuous Monitoring to detect fraud early.
✔ Strengthen Internal Controls to minimize fraud risks.
✔ Invest in Employee Training and Fraud Awareness programs.
✔ Leverage AI, blockchain, and machine learning for fraud detection.
✔ Develop a Fraud Response Plan to act swiftly in case of incidents.
References
- DiLorenzo, C. (2015). Creating a Fraud Risk Assessment and Implementing a Continuous Monitoring Program.
- ACFE Report to the Nations (2024).
- COSO Framework (2013).
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (2002).
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) – Fraud Prevention Guidelines.
- Top Strategies for Detecting and Preventing Fraud in Organizations